SEO Rules
Engine Specifications
- URL
- Schema.org Structured Data
- HTTP Status Codes
- Mobile Adaptation
- Core Web Vitals
- Hreflang Tags
- Noindex Tags
- JS Loading
SEO Elements
Website Content
The role of the Nofollow tag in SEO is primarily to control how search engine crawlers handle links in webpages. The Nofollow tag can help websites manage and optimize link traffic, while following search engine best practices and guidelines, ensuring the website's credibility and ranking performance in search engines. The following are the importance and impact of the nofollow tag in SEO:
1. Control link traffic
Prevent link loss: The nofollow tag can prevent search engines from passing weight (PageRank) through that link. This is very useful for situations where you need to prevent weight transfer, such as user-generated content (UGC) or advertising pages.
2. Avoid manipulation of rankings
Follow Google guidelines: According to Google's recommendations, the nofollow tag is used to mark links that do not contribute value to webpage rankings, such as paid links or untrusted content. This helps comply with search engine guidelines and avoid penalties for improper behavior.
3. Increase website security
Prevent linking to unsafe websites: By using the nofollow tag, you can avoid having your website linked to unsafe or malicious websites, thus protecting the website's security and reputation.
4. SEO best practices
Use appropriately: Use the nofollow tag cautiously, ensuring it is used for appropriate link types. Overuse of the nofollow tag may affect the overall link structure of webpages and SEO optimization effectiveness.
Specifications and best practices:
1. Use appropriately:
Paid links: When links are advertisements or generated after payment, but you don't want them to affect SEO, you can use the nofollow tag.
User-generated content (UGC): For example, user-generated links in comment sections or forums, to avoid uncontrolled outbound links from affecting performance, nofollow can be used.
Untrustworthy links: When linking to websites you don't trust or unknown content pages, you can also consider using the nofollow tag.
2. Marking method:
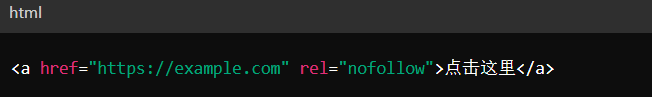
In HTML, the nofollow tag is usually used with the <a> tag, specified by adding the rel="nofollow" attribute.
Example:
3. Correct syntax and position:
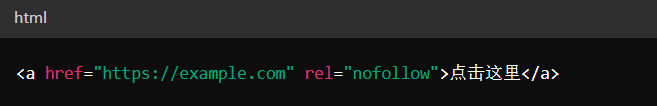
The nofollow tag should be specified in the rel attribute within the <a> tag, ensuring correct syntax so that search engines can parse and execute correctly.
Example:
Notes:
1. Use cautiously:
Avoid abusing the nofollow tag. Using too many nofollow tags may affect the overall link structure of pages and SEO optimization effectiveness.
2. Not to be used on important internal links:
Do not use the nofollow tag on important internal links. These links usually point to core content or pages and should optimize and pass webpage weight through internal links.
3. Used in conjunction with other rel attributes:
If you need to mark nofollow along with other relationships (such as sponsored for marking paid links), you can combine them in the rel attribute, but ensure accuracy and consistency of the markings.
4. SEO tool validation:
Use SEO tools (such as Google Search Console) to validate the correct application of nofollow tags to ensure they can influence search engine behavior as expected.
Detailed Specifications:
1. Add nofollow tag to URLs that do not need search engine crawling and tracking;
2. Add nofollow tag to outbound links from the site that do not need search engine tracking;
3. The nofollow attribute needs to be used correctly, included within the A tag;
Example:
<a class="Footer_footer_menu_a__yFJG_" href="https://connect.studentbeans.com/v4/hosted/anker/us?ref=footer" rel="nofollow">Education Discount</a>
Reference Website:
Official Google Explanation:
For certain links on your website, you may need to explain to Google the relationship between your website and the linked page. To do this, use one of the following rel attribute values in the <a> tag.
For regular links that you want Google to extract and parse without any conditions, you do not need to add the rel attribute.

For other links, use one or more of the following values:
1. rel="sponsored"
Use the sponsored value to mark advertising links or paid placement links (commonly known as "paid links").
<a rel="sponsored" href="https://cheese.example.com/Appenzeller_cheese">Appenzeller</a>
Note: For this type of link, the nofollow attribute was previously recommended, and you can still use that attribute for marking, but it is now more recommended to use the sponsored tag.
2. rel="ugc"
It is recommended that you use the ugc value to mark links to user-generated content (such as comments and forum posts).
<a rel="ugc" href="https://cheese.example.com/Appenzeller_cheese">Appenzeller</a>
If you want to acknowledge and reward trusted contributors (members or users who consistently make high-quality contributions), you can remove this attribute from links they post.
3. rel="nofollow"
If other values do not apply and you want Google to not follow outbound links from your website or not crawl the linked page from your website, use the nofollow value. For links within your website, use the robots.txt disallow rule.
<a rel="nofollow" href="https://cheese.example.com/Appenzeller_cheese">Appenzeller</a>
4. Multiple values
You can specify multiple rel values using a list separated by spaces or English commas. Example:
<p>I love <a rel="ugc nofollow" href="https://cheese.example.com/Appenzeller_cheese">Appenzeller</a> cheese.</p>
<p>I hate <a rel="ugc,nofollow" href="https://cheese.example.com/blue_cheese">Blue</a> cheese.</p>
Google typically does not follow links marked with these rel attributes. Please note that linked pages may also be found through other means (such as sitemaps or outbound links from other websites), so they may still be crawled. These rel attributes can only be used in <a> elements that Google can crawl, except for nofollow, which can also be used as a robots meta tag.
If you don't want Google to extract links pointing to your internal webpages, use the robots.txt disallow rule.
If you don't want Google to index a particular webpage, allow crawling and use the noindex robots rule.