SEO Rules
Engine Specifications
- URL
- Schema.org Structured Data
- HTTP Status Codes
- Mobile Adaptation
- Core Web Vitals
- Hreflang Tags
- Noindex Tags
- JS Loading
SEO Elements
Website Content
The importance of webpage size to SEO mainly manifests in webpage loading speed and user experience. By effectively optimizing webpage size and loading speed, you can improve your website's ranking and visibility in search engines, while improving user access experience, thereby achieving better SEO results and website operational effectiveness. The following are the impact and importance of webpage size on SEO:
1. Webpage Loading Speed
Search engine ranking factor: Google and other search engines have confirmed that webpage loading speed is one of the important factors affecting search rankings. Fast-loading webpages can improve user experience and may receive better search engine rankings.
Mobile-first indexing: With the promotion of Google's mobile-first indexing, webpage loading speed on mobile devices is particularly important. Fast-loading mobile-friendly webpages can improve rankings in mobile search results.
2. User Experience
Reduce bounce rate: Users tend to spend shorter time on webpages with slow loading speeds, resulting in high bounce rates. Optimizing webpage size and loading speed can improve user experience, reduce bounce rate, and increase page browsing time.
Improve page interaction: Fast-loading webpages can respond more quickly to user interactions, such as clicks and scrolls, improving user interaction experience and satisfaction.
3. SEO Best Practices
Webpage experience metrics: Google treats user experience as one of the important considerations in its algorithm, including loading speed and page interactivity. Therefore, optimizing webpage size is part of following best practices.
Recommendations for implementing webpage size optimization:
1. Image and media optimization: Compress and optimize images, videos, and other media files to ensure they are appropriately sized and do not affect webpage loading speed.
2. Code streamlining: Reduce redundancy and unnecessary parts in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code to speed up webpage loading time.
3. Use CDN (Content Delivery Network): Utilize CDN to improve webpage content distribution speed and reduce the time from user request to response.
4. Responsive design: Adopt responsive webpage design to dynamically adjust content and image presentation based on user devices and screen sizes, optimizing user experience.
The following are some suggestions regarding webpage size appropriateness and optimization:
1. Appropriate Webpage Size
(1) General recommendations:
Total size: Try to keep the entire webpage size within 1MB, especially important for mobile device users.
Initial loading content: Ensure the webpage's initial loading content completes within a few seconds to provide fast user experience.
(2) Specific element size recommendations:
Image size: Individual image size should be controlled between tens of KB to hundreds of KB. Use tools to compress images, ensuring file size reduction without losing visual quality.
Scripts and stylesheets: Minimize JavaScript and CSS file sizes as much as possible, avoiding redundant or unused code.
Font files: Use appropriate font formats (such as WOFF2), and ensure font file sizes are reasonable to reduce impact on loading time.
2. Methods for webpage size optimization
(1) Image optimization:
Use appropriate image formats (such as JPEG, PNG).
Compress images to reduce file size, using online tools or graphics editing software.
Use image lazy loading technology to delay loading images not visible in the viewport, speeding up initial loading time.
(2) Code optimization:
Streamline HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code, removing spaces, comments, and unnecessary code.
Combine and compress CSS and JavaScript files to reduce HTTP request counts.
(3) Server and resource management:
Use Content Delivery Network (CDN) to accelerate page resource delivery.
Optimize server response time, ensuring the server can quickly process and transmit webpage content.
(4) Responsive design:
Adopt responsive webpage design to adapt to different devices and screen sizes, reducing unnecessary content loading and display.
(5) Tools and monitoring:
Use tools such as Google PageSpeed Insights, WebPageTest, etc., to test webpage loading speed and optimize adjustments based on test results.
Regularly monitor website performance and user experience, making further optimizations based on data.
Example:
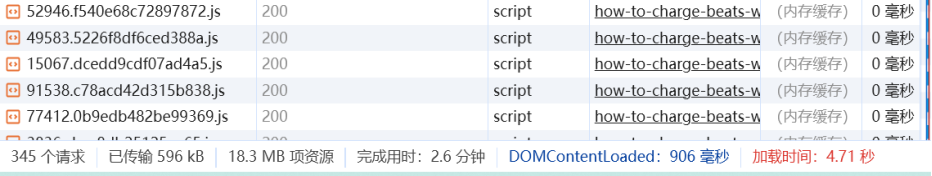
Reference Website: