SEO Rules
Engine Specifications
- URL
- Schema.org Structured Data
- HTTP Status Codes
- Mobile Adaptation
- Core Web Vitals
- Hreflang Tags
- Noindex Tags
- JS Loading
SEO Elements
Website Content
Robots.txt is a text file placed in the root directory of a website to inform search engines which pages can or cannot be crawled. It can effectively control Google bot crawling behavior, optimize crawling and indexing processes, protect website privacy and security, and improve the overall SEO performance of the website. Properly configuring the robots.txt file is crucial for enhancing the website's ranking and performance in Google search results.
Its importance in SEO:
Crawl Control: Through the robots.txt file, website administrators can control which parts of the website search engine spiders can crawl. This helps avoid crawling unnecessary pages and saves crawl budget.
Protect Sensitive Information: It can prevent search engines from crawling and indexing sensitive information or pages that are not intended to be public, such as admin panels, user privacy information, etc.
Improve Website Performance: Avoid crawling dynamically generated pages or duplicate content, which can reduce server load, improve website performance and user experience.
Optimize Crawl Frequency: Through the robots.txt file, you can guide search engines to crawl important pages more frequently, improving the indexing and ranking of these pages.
Standardize Website Structure: Helps search engines understand the website structure, improving the indexing efficiency and accuracy of the website.
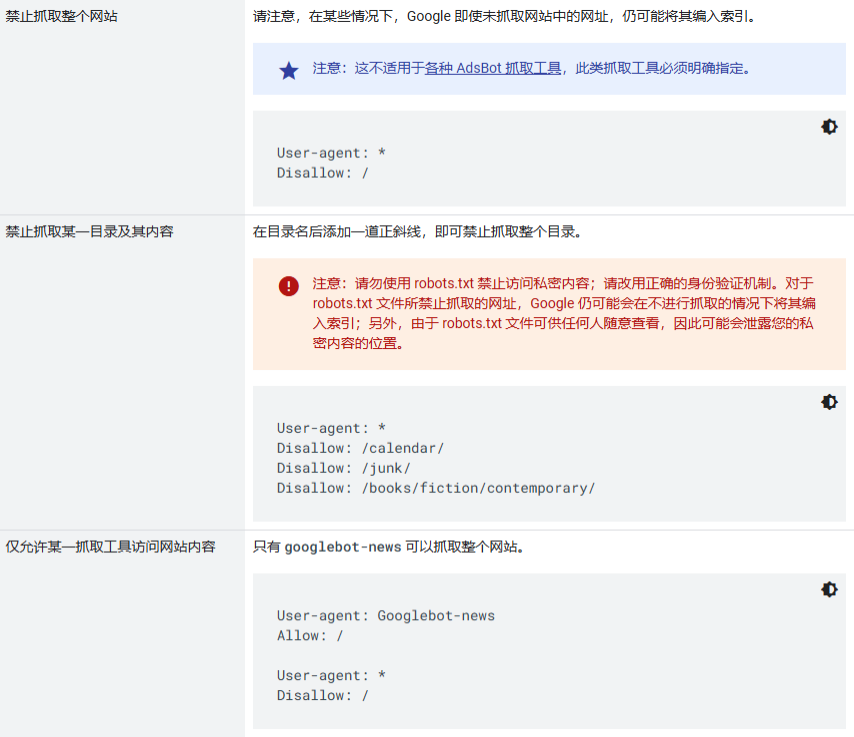
Basic Format of Robots.txt File
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin/
Allow: /public/
Sitemap: http://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
User-agent: Specifies the search engine spider, * means all search engines.
Disallow: Specifies the paths not allowed to be crawled.
Allow: Specifies the paths allowed to be crawled (usually used to override disallow rules in certain situations).
Sitemap: Specifies the URL of the sitemap, helping search engines better index website content.
Detailed Specifications:
1. The robots.txt file should be located in the root directory of the website;
2. The file consists of one or more rules. Each rule can prohibit or allow all or specific crawlers;
3. By default, all files are crawlable if not explicitly disallowed
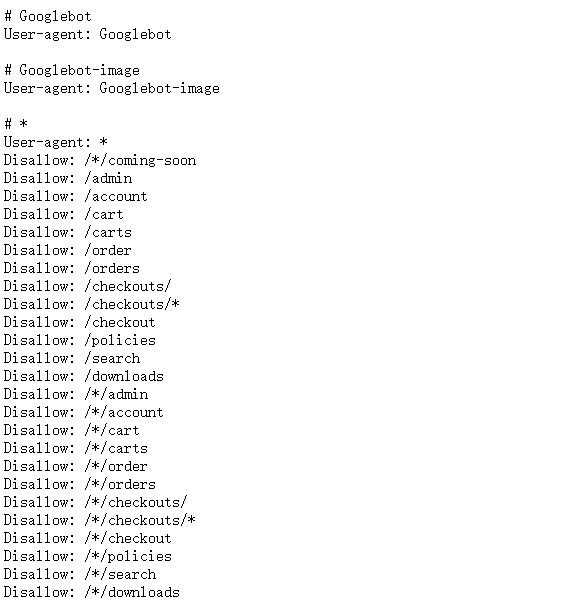
Example:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /*/coming-soon
Disallow: /admin
Disallow: /account
Disallow: /cart
Reference Website:
Official Google Explanation:
1. What is the purpose of a robots.txt file?
The robots.txt file is primarily used to manage crawler traffic flowing to your website, and is typically used to block Google from accessing certain files (depending on file type):
(1) Web pages: For web pages (including HTML, PDF, or other non-media formats that Google can read), you can use the robots.txt file to manage crawl traffic in the following situations: You believe requests from Google bots could overload your server; or you don't want Google to crawl unimportant or similar web pages on your site.
If you use a robots.txt file to block Google from crawling your web page, its URL may still appear in search results, but the search results will not include descriptions of that page. Additionally, image files, video files, PDF files, and other non-HTML files embedded in blocked web pages will be excluded from crawling unless other allowed pages reference these files. If you see a search result corresponding to your web page and want to fix it, remove the robots.txt entry that blocks the page. If you want to completely hide the page from Google search results, use other methods instead.
Warning: If you don't want your web page (including PDF and other text-based formats supported by Google) to appear in Google search results, do not use the robots.txt file as a method to hide the page. If other web pages link to your page using descriptive text, Google can still index your URL without visiting your page. If you want to block your page from search results, use other methods such as password protection or noindex.
(2) Media files: You can use the robots.txt file to manage crawl traffic and prevent images, videos, and audio files from appearing in Google search results. This does not prevent other web pages or users from linking to your image/video/audio files.
(3) If you believe skipping resources such as unimportant images, scripts, or style sheets during page loading won't significantly impact the page, you can use the robots.txt file to block such resources. However, if missing these resources makes it difficult for Google bots to interpret the web page, do not block these resources, otherwise Google will not be able to effectively analyze pages that rely on these resources.
2. Limitations of robots.txt files
Before creating or modifying a robots.txt file, you should understand the limitations of this URL blocking method. Depending on your goals and specific situation, you may need to consider other mechanisms to ensure search engines cannot find your URL on the web.
(1) Not all search engines support robots.txt rules.
Commands in robots.txt files cannot force crawler behavior; it is up to the crawler to decide whether to follow these commands. Googlebot and other legitimate web crawlers will follow commands in robots.txt files, but other crawlers may not. Therefore, if you want to ensure specific information is not crawled by web crawlers, we recommend using other blocking methods, such as password protecting private files on your server.
(2) Different crawlers may parse syntax in different ways.
Although legitimate web crawlers follow rules in robots.txt files, different crawlers may parse these rules differently. You need to familiarize yourself with the correct syntax for different web crawlers, as some crawlers may not understand certain commands.
(3) If links to pages blocked by robots.txt files exist on other websites, those pages may still be indexed.
Even though Google will not crawl or index content blocked by robots.txt files, if there are links pointing to forbidden URLs from other locations on the web, we may still discover those URLs and index them. Therefore, the relevant URLs and other publicly displayed information (such as anchor text in related page links) may still appear in Google search results. To properly block your URL from appearing in Google search results, you should set up password protection for files on your server, use noindex meta tags or response headers, or completely remove the page.
3. Practical robots.txt rules