SEO Rules
Engine Specifications
- URL
- Schema.org Structured Data
- HTTP Status Codes
- Mobile Adaptation
- Core Web Vitals
- Hreflang Tags
- Noindex Tags
- JS Loading
SEO Elements
Website Content
The importance of Schema.org structured data for SEO lies in improving search engines' understanding of website content, enriching search result display formats, increasing click-through rates, and local search rankings. By selecting appropriate Schema types, correctly embedding and validating structured data, websites can significantly enhance their performance in search engines, thereby attracting more quality traffic.
Here is a detailed explanation and specific implementation steps:
1. Improve Search Engine Understanding of Content
Better Semantic Understanding: Schema.org provides a set of standard tags that help search engines better understand the semantics of web page content. By using structured data, search engines can more accurately parse website content and topics.
Data Integration: Structured data makes different types of content (such as articles, products, events, reviews, etc.) more structured, making it easier for search engines to integrate and display relevant information.
2. Rich Search Result Display
Enhanced Search Results: By using Schema.org structured data, websites can achieve rich search result display formats, such as rich snippets, knowledge graphs, etc. These display formats can include star ratings, product prices, event times, video previews, etc., attracting user clicks.
Increase Click-Through Rate (CTR): Rich search result display formats are often more eye-catching than ordinary search results, thereby increasing click-through rates.
3. Improve Local Search Rankings
Local Search Optimization: For local businesses, Schema.org's LocalBusiness type can provide detailed business information, such as addresses, business hours, phone numbers, etc., helping to improve rankings in local search results.
4. Enhance Social Media Display
Social Media Integration: Structured data is not only useful for search engines but can also enhance content presentation on social media. Social platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn can use structured data to generate richer share cards, improving content sharing and click-through rates.
Implementation Steps for Schema.org Structured Data
1. Choose Appropriate Schema Type
Based on your website content, choose an appropriate Schema.org type. For example, use Article for blog posts, Product for products, LocalBusiness for local businesses, etc.
You can find detailed type and property documentation on the Schema.org official website.
2. Embed Structured Data
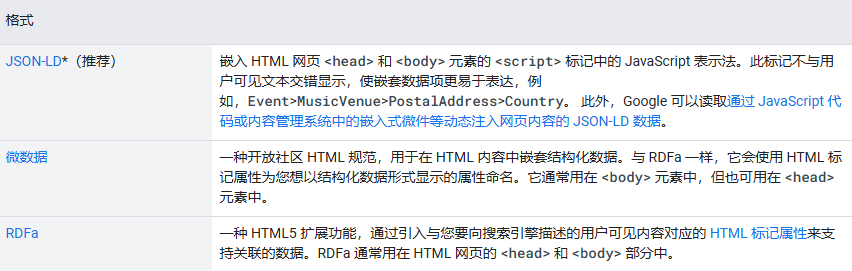
JSON-LD (recommended): Embed structured data in JSON-LD format in the <head> section of the webpage. The JSON-LD format is easy to maintain and does not affect HTML structure.
Microdata: Embed structured data in HTML tags. This method embeds structured data directly into content tags, which is more complex.
RDFa: Similar to Microdata, embed structured data in HTML tags, but using RDF syntax.
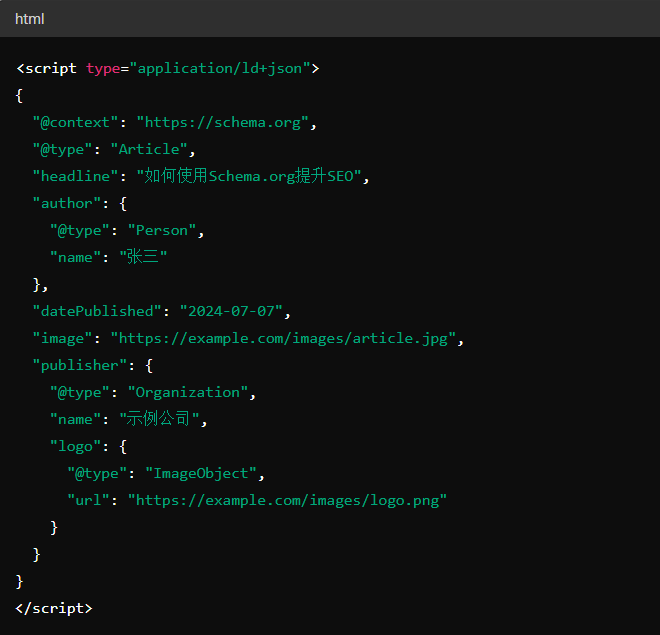
For example, using JSON-LD to add structured data to a blog post:
3. Validate Structured Data
Use Google's structured data testing tool to verify that your embedded structured data is correct.
Ensure all required attributes are filled in and data format is correct.
4. Monitor Structured Data Performance
In Google Search Console, view structured data reports and monitor any errors or warnings.
Check rich snippet display and click-through rate changes to evaluate the actual effect of structured data.
Detailed Specifications:
1. Supported formats: JSON-LD (recommended), microdata, RDFa;
2. Prohibit using robots.txt, noindex, or any other access control methods to block Googlebot from accessing your structured data pages;
3. Ensure all required attributes listed in the corresponding rich result type documentation are complete;
4. Place structured data on the page that describes the content;
5. When there are multiple items on a webpage, you can either nest multiple items or specify each item separately;
Reference URL:
Official Google Explanation:
Google Search strives to understand web page content. You can add structured data to web pages to provide Google with clear clues about the meaning of the page, helping us understand it. Structured data is a standardized format that provides information about a web page and categorizes its content; for example, a recipe page would have ingredients, cooking time and temperature, calories, and other information.
1. Why add structured data to web pages?
Adding structured data allows you to obtain search results that are more attractive to users and may encourage more interaction with your website, which is rich results. Here are some case studies of websites that have implemented structured data:
①Rotten Tomatoes added structured data to 100,000 unique web pages. Results showed that pages with structured data had 25% higher click-through rates than pages without structured data.
②Food Network converted 80% of its web pages to search-enabled, resulting in a 35% increase in traffic.
③Rakuten found that users spent 1.5 times more time on pages with structured data than on pages without it, and engagement rates on AMP pages with rich results features were 3.6 times higher than on AMP pages without these features.
④Nestlé measured that pages displayed as rich results in search received 82% higher click-through rates than those not displayed as rich results.
2. How structured data works in Google Search
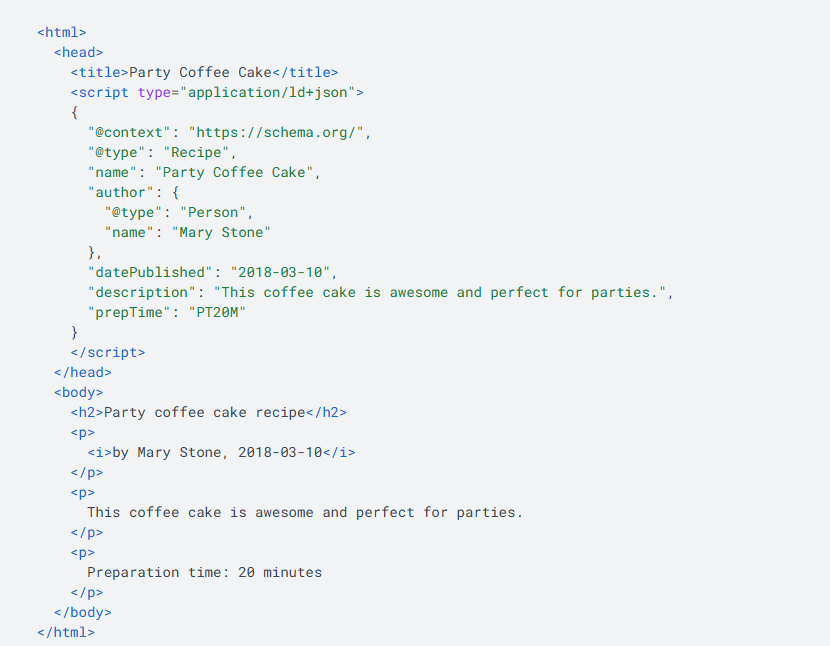
Google uses structured data found on the web to understand web page content and collect general information about the web and world, such as information about people, books, or companies in tags. For example, the following JSON-LD structured data snippet may appear on a recipe page, describing the recipe's title, author, and other details:
Google Search also uses structured data to enable special search result features and enhancements. For example, a recipe page containing valid structured data can appear in image search results as follows:
Structured Data:

Search Result Presentation:
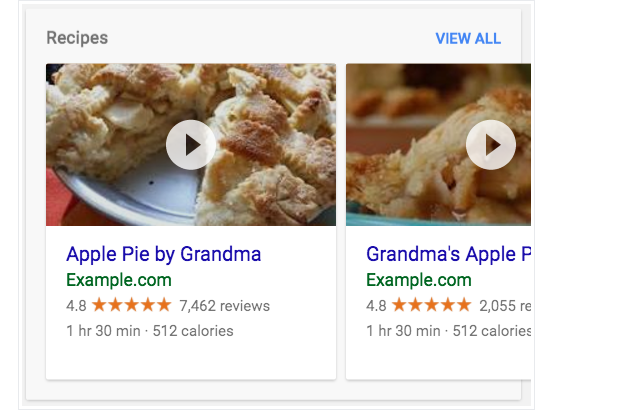
3. Supported Formats