SEO Rules
Engine Specifications
- URL
- Schema.org Structured Data
- HTTP Status Codes
- Mobile Adaptation
- Core Web Vitals
- Hreflang Tags
- Noindex Tags
- JS Loading
SEO Elements
Website Content
The importance of implementing www redirects for SEO is reflected in aspects such as avoiding duplicate content issues, improving user experience, increasing search engine crawling efficiency, and facilitating data analysis. Correctly implementing www redirects can concentrate page authority, improve search engine rankings, enhance user trust, and ensure data analysis consistency. This is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Avoid Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate Content: If the same website can be accessed through both URLs with "www" (such as www.example.com) and URLs without "www" (such as example.com), search engines may treat them as two different websites, resulting in duplicate content issues. This dilutes page authority and affects rankings.
Concentrating Authority: Through redirects, concentrating all traffic to one version can avoid authority dispersion and improve search engines' evaluation of pages.
2. Improve User Experience
Consistency: Users will have a consistent experience when visiting the website. Whether they enter www.example.com or example.com, they will be redirected to the same URL, avoiding confusion.
Brand Image: Consistent URL structure helps establish a consistent brand image and enhances user trust in the website.
3. Improve Search Engine Crawling Efficiency
Crawling Budget: Search engines have a crawling budget, meaning they have a limited number of pages they can crawl on your website within a certain time period. By unifying URLs, you can ensure search engine spiders concentrate their crawling budget on one version, improving crawling efficiency.
4. Facilitate Data Analysis
Data Consistency: In tools such as Google Analytics, all traffic will be recorded to the same URL version, avoiding data confusion and helping to more accurately analyze traffic and user behavior.
Steps for Implementing www Redirects
1. Choose Preferred Domain: Decide whether to use the "www" version or the non-"www" version as your preferred domain. For example, choose to use www.example.com or example.com.
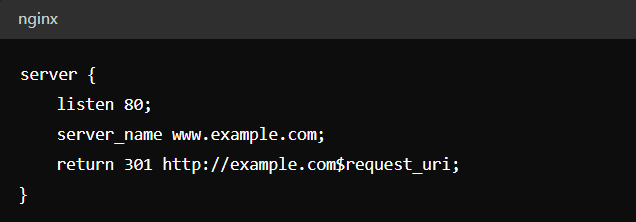
2. Set up 301 Redirects: Set up 301 permanent redirects on the server to redirect all traffic from the non-preferred domain to the preferred domain. This can be achieved by modifying server configuration files (such as Apache's .htaccess or Nginx's nginx.conf).
(1) Redirect non-"www" to "www":
Apache Example:
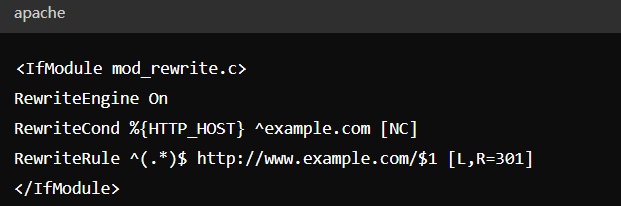
Nginx Example:
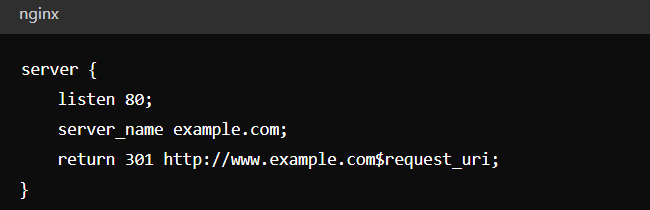
Redirect "www" to non-"www":
Apache Example:
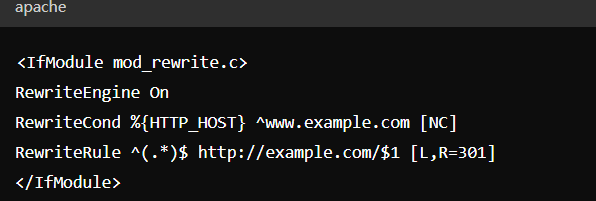
Nginx Example:
3. Update Google Search Console: Add and verify your chosen preferred domain in Google Search Console. Ensure you select the preferred domain in "Settings".
4. Update Sitemap: Ensure the URLs used in the sitemap are consistent with your preferred domain and submit the updated sitemap in Google Search Console.
5. Check Internal Links: Update all internal links to ensure they point to the preferred domain, avoiding the use of different URL versions between pages.
6. Notify Search Engines: Notify search engines that your website has set a preferred domain by submitting sitemaps and crawl requests.
Detailed Specifications:
1. Add DNS resolution for the www domain;
2. To ensure homepage uniqueness, it is recommended to 301 redirect the non-www domain to the www domain;
Example:
www resolution: https://www.haoqiebike.com/
Reference Website: