SEO Rules
Engine Specifications
- URL
- Schema.org Structured Data
- HTTP Status Codes
- Mobile Adaptation
- Core Web Vitals
- Hreflang Tags
- Noindex Tags
- JS Loading
SEO Elements
Website Content
The Noindex tag plays an important role in SEO, especially in managing and optimizing the indexing behavior of website content. Proper and correct use of the Noindex tag can help websites effectively solve issues such as duplicate content, manage temporary pages, and protect sensitive content, thereby improving overall search engine rankings and user experience. However, it should be noted that excessive use or incorrect use of the Noindex tag may have negative effects on SEO, so it should be used with careful consideration and operation according to specific situations.
Correct use of the <meta name="robots" content="noindex"> tag is very important, as it can instruct search engines not to index specific pages. This is particularly useful in the following situations:
1. Prevent duplicate content from being indexed
Dynamic generation of pages: Some websites may dynamically generate a large amount of content, such as search result pages, tag pages, or filter pages. These pages usually have no practical value, so the Noindex tag can be used to prevent them from being indexed, thus
avoiding duplicate content issues.
2. Managing test pages or temporary pages
Test pages: When developing or testing new features, some temporary pages may be created. These pages are usually not intended to be indexed by search engines, to avoid affecting the overall SEO performance of the website. By adding the Noindex tag, these pages can be prevented from being indexed in search engine results.
3. Hiding sensitive content or pages
Paid content: If a website provides paid content or services and does not want this content to be accessed by non-paying users, the Noindex tag can be used to ensure that these pages do not appear in search results, protecting the uniqueness and value of the paid content.
How to properly use the Noindex tag:
1. Add the tag to the page header:
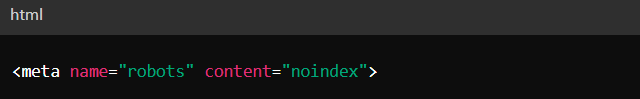
This tag should be placed within the <head> section of the page. It tells search engines not to index this page.
2. Combine with other tags:
Nofollow tag: If the page contains external links, you can combine it with <meta name="robots" content="nofollow"> to prevent search engines from following these links.
Noarchive tag: <meta name="robots" content="noarchive"> can prevent search engines from caching copies of the page.
3. Confirm usage scenarios:
Ensure the Noindex tag is used in appropriate situations. Overuse or incorrect use of the Noindex tag may lead to unexpected SEO impacts, such as ranking drops or pages being mistakenly considered low-quality content.
4. Verify tag effectiveness:
Use tools like Google Search Console to verify the effectiveness of the Noindex tag. Google Search Console can show which pages are marked with Noindex, ensuring they work as expected.
5. Notes:
Use with caution: Make sure to use the Noindex tag only when really needed, to prevent unexpected ranking drops or search engine indexing issues.
Avoid abuse: Avoid applying the Noindex tag to important content or core pages, as this could lead to ranking drops or reduced website traffic.
Detailed Specifications:
1. Two ways to implement noindex: implement it as a meta tag, or as an HTTP response header;
2. Meta tag format: <meta name="robots" content="noindex" />;
3. X-Robots-Tag HTTP header returning noindex or none: X-Robots-Tag: noindex;
4. Ensure noindex rules are visible to Googlebot;
Example:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, nofollow" />
Official Google Explanation:
noindex is a rule set that includes <meta> tags or HTTP response headers, used to prevent search engines that support the noindex rule (such as Google) from indexing content. When Googlebot crawls the webpage and discovers the tag or header, Google will completely block the webpage from appearing in Google search results, regardless of whether other websites link to the webpage.
1. Implementing noindex
There are two ways to implement noindex: implement it as a <meta> tag, or as an HTTP response header. Both methods have the same effect, so choose the one that is more convenient for your website and better suited to the corresponding content type. Google does not support specifying noindex rules in the robots.txt file.
You can also combine noindex rules with other rules that control indexing. For example, you can combine nofollow hints with noindex rules: <meta name="robots" content="noindex, nofollow" />.
<meta> Tag
To prevent all search engines that support the noindex rule from indexing a webpage on your site, add the following <meta> tag to the <head> section of the webpage:
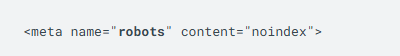
To only block Google's web crawler from indexing the webpage, use the following meta tag:
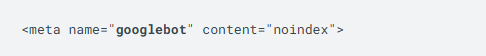
Please note that some search engines may have different interpretations of noindex rules. Therefore, your webpage may still appear in results from other search engines.
2. HTTP Response Headers
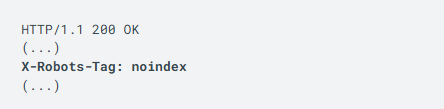
Instead of a <meta> tag, you can return an X-Robots-Tag HTTP header with a value of noindex or none in the response. Response headers can be used for non-HTML resources, such as PDF files, video files, and image files. Below is an example of an HTTP response that contains an X-Robots-Tag header to instruct search engines not to index a webpage:
3. Debugging noindex Issues
We must crawl your webpage to see the <meta> tags and HTTP headers. If a webpage still appears in search results, it may be because we have not crawled the webpage since you added the noindex rule. Depending on the webpage's importance on the internet, Googlebot may need several months to revisit the webpage. You can use the URL inspection tool to request Google to recrawl your webpage.
Additionally, it may be because the robots.txt file prevents Google's web crawler from accessing the URL, so these crawlers cannot discover this tag. To allow Google to access your webpage, you must modify the robots.txt file.
Finally, ensure that noindex rules are visible to Googlebot. To test whether your noindex implementation is correct, use the URL inspection tool to view the HTML that Googlebot receives when crawling the webpage. You can also use the "Index Coverage" report in Search Console to monitor webpages on your site where Googlebot discovers noindex rules.